Awesome Info About How To Write A Noun Clause

It can also begin with the subordinating.
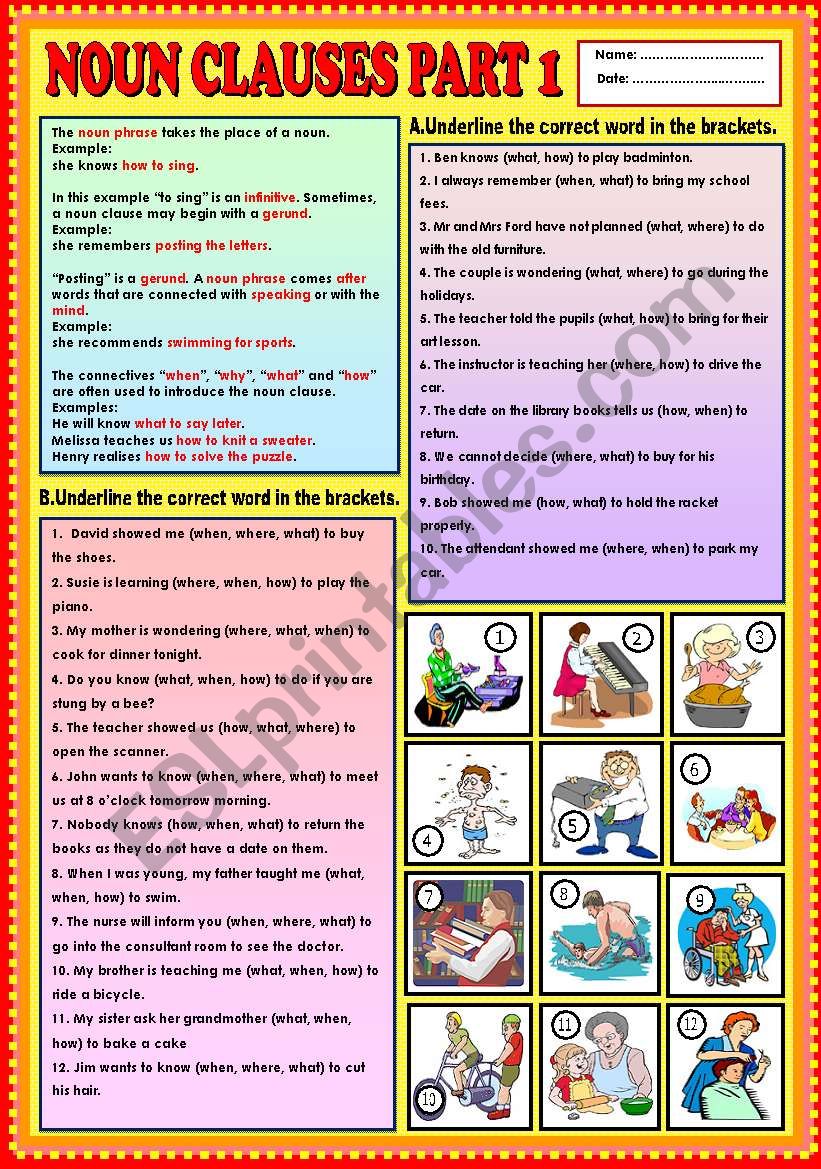
How to write a noun clause. A noun clause gets its name because it is simply a clause that acts like a noun. A noun clause is a dependent clause that contains a subject and a verb. A noun clause usually begins with a relative pronoun like that, which, who, whoever, whomever, whose, what, or whatsoever.
They are dependent clauses, meaning they must always be paired. I like what he said. Enhance your writing with noun clauses | coursera.
It can be the subject of a sentence, an object, or a complement. A noun clause cannot stand alone because it is not a. Different types of noun clauses.
A clause is any group of words that contains both a subject and a verb, but noun clauses are a. To understand what a noun clause is, let’s begin with its individual parts. What is a noun clause?
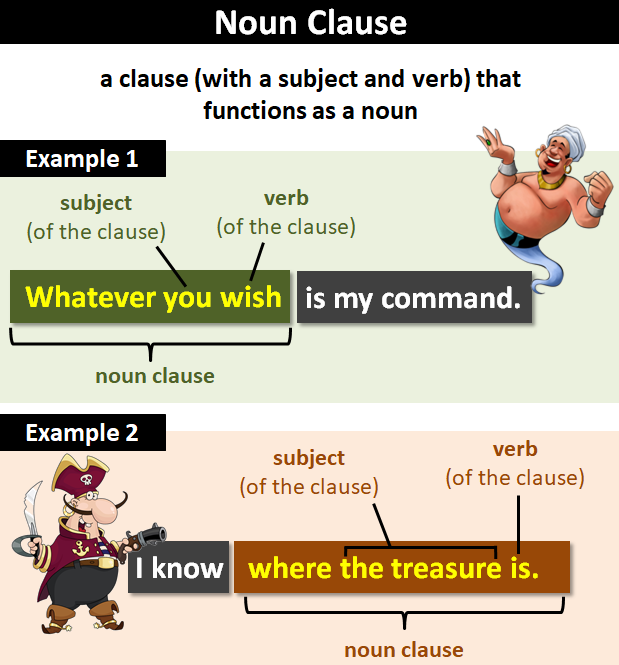
A noun clause functions as noun in a sentence. A noun clause is a dependent (or subordinate clause) that works as a noun. This course is part of learn english:
To better understand how noun clauses work, it’s essential to recognize and familiarize yourself with their various functions within. A noun clause starts with the following subordinating conjunctions: The concise oxford dictionary of linguistics explains a noun clause as “a clause whose syntactic role is seen as like that of a noun or noun phrase ”, and the collins dictionary.
What you do, clearly. Writing effectively with complex sentences specialization. For example, table is a.
Here’s an example of a. A noun clause is a dependent clause that functions as a noun in a sentence. Complement of a verb or adjective.
Clauses can perform three distinct functions: How to identify noun clauses. A noun is a word that refers to an object or thing.
What he bought was awful: Find the sentence’s dependent clause. What he said = object.